AdBlue® is a solution compatible with Diesel engine Euro IV,V and VI, which contains demineralized water and urea CO(NH2)2 with a concentration of 31.8%- 33.2%
( according to the ISO 22241-1 International Standard) and it is useful for the majority of vehicles and agricultural equipment.
AdBlue® is no fuel, neither an additive and it is not mixed with the gas, but it must be injected into the evacuation system in order to reduce the pollution. It is a key product for all vehicles using the SCR Technology( Selective Catalytic Reduction) which reduces the toxic emissions, especially the nitrogen oxides with almost 80%.
The AdBlue® consumption is around 3-5 liter per 100 liter of gas ( for Euro V) and around 6-9 liter (for Euro VI).
It is an ecological liquid, non-toxic, biodegradable, safe and easy to manipulate.
This solution is chemically stable, with a point of freeze at -11 °C and the optimal storage temperature of 25°C, without direct sunlight exposure.
Moreover, by using a high quality, certified AdBlue® you can have additional advantages as the fuel consumption reduction with almost 5%.
AdBlue® Benefits
By injecting AdBlue® into the SCR catalytic converter, all harmful nitrogen oxides( NOx) are instantly transformed into innoxious nitrogen and water.
It is important to have always a sufficient amount of AdBlue® in the tank of a car.
Otherwise, if a vehicle using a SCR-system is being operated without AdBlue®, the SCR-equipment has a high risk of being damaged.
AdBlue® is a very pure solution, biodegradable, that is not damaging the environment, non-toxic and easy to handle liquid.
At -11° AdBlue® freezes and at 70°C decomposes into ammonia. Above 30° AdBlue® starts to decompose.
Keeping the solution in proper conditions (not exposed under the direct sunlight) will ensure you the quality of the product.
AdBlue®
Dinamic Efficiency
AdBlue® is a key product for all vehicles using SCR technology
Quality and Efficiency
AdBlue® reduces fuel consumption by up to 5%. This process takes place in two stages: elimination of particles and reduction of nitrogen oxides


AdBlue® reduces the fuel consumption up to 5%.
By using a high quality, certified AdBlue® you can have additional advantages as the fuel consumption reduction with almost 5%.
This process has 2 stages: the particles elimination and reduction of nitrogen oxides
1.The particles elimination
The first step of treating the exhaust gases is particles elimination.
In order to clean the combustion pollutants from the diesel engines exhaust they are used additional systems of treating the exhausting gases.
The first step is the oxidation catalytic convertor. Here, the pollutants are transformed into harmless exhaust gases components.
The second step consists on soot cleaning from the exhaust gases by the gas particles filter. The cleaning is produced by burning the incorporated particles and it can be done if the temperature of the particles filter is at least 350°C.
In order to actively burn the filter, the engine command unit increases the exhausting temperature at 600°C. An immediate consequence is a short raise of fuel consumption and, thus, the raise with 9% of CO2 emissions.
In a new car, the particles filter has an efficiency of almost 100%, so the gas does not contain any trace of soot.
II.Reduction of nitrogen oxides
In order to reduce the nitrogen oxides emissions (NOx), in this stage can be used two technologies that can act in a cumulated manner: the NOx stocking catalytic convertor and the SCR catalytic convertor(Selective Catalytic Reduction).
The NOx stocking catalytic convertor aim is to eliminate the nitrogen oxides from the exhausting gases and their stocking until it reaches its exploitation capacity.
The stocked nitrogen oxides are transformed into carbon dioxide( CO2) and nitrogen(N2) , which are neutral substances. After this process, the NOx catalytic convertor starts again its functioning.
The stocking catalytic convertor can stock nitrogen oxides only at temperatures between 150 și 500°C. Thus, the start at cold is very important, the engine could’nt yet reach the necessary temperature. This thing is quite opposite with the normal functioning, when the engine reaches the maximum efficiency from around 80% at the functioning temperature of 300-400°C. The vehicle increased consumption for the reconstitution of nitrogen oxides deposit is around 2%.
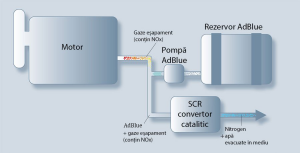
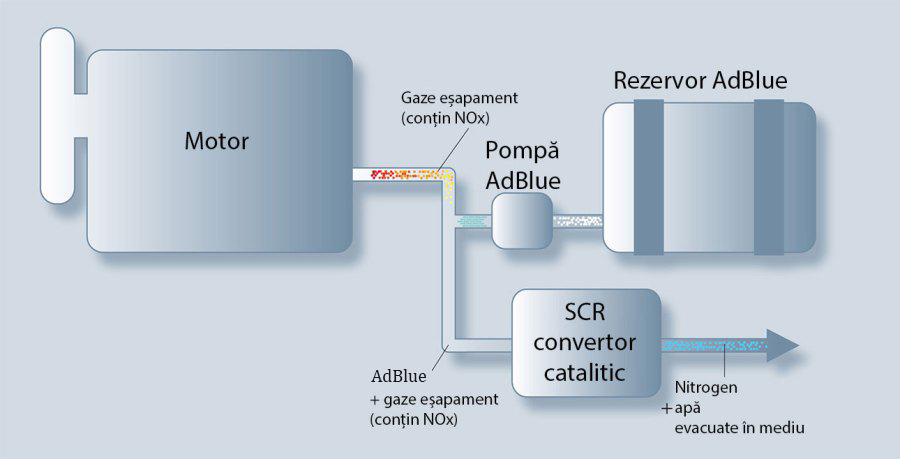
Within the SCR( Selective Catalytic Reduction) catalytic convertor, the nitrogen oxides emissions are transformed by adding the AdBlue® sprayed into the exhausting flux into the neutral components of nitrogen(N2), water and carbon dioxide(CO2).
Only at temperatures higher than 200°C are recorded significant transformation rates of nitrogen oxides.
When the engine and the exhausting system are situated at the functioning temperature, the SCR catalytic convertor removes up to 90% from the nitrogen oxides emissions from the exhausting gases.
Its high efficiency level makes possible the burning adjustment for a reduced consumption and, thus, lower carbon dioxide emissions. This means that a fuel economy of up to 5% it is possible.
(Informations from the 2016 annual report of German Auto Industry VDA).
AdBlue®
reduces the fuel consumption up to 5%
Questions and answers
When you have to fill again the tank with AdBlue®?
The AdBlue® tank must not be never empty.
The vehicle monitors the AdBlue level from the tank and informs the driver in advance, many times that he has to add more solution.
How it works the SCR technlogy (part I)?
The SCR technology or the selective catalytic reduction represents the process through which the oxides of nitrogen from the exhaust gases are reduced, by using a high quality AdBlue®.
The SCR system consists in a metal catalyst installed into the car exhausting system and the AdBlue® which helps the harmful emissions(NOx) to be transformed into atmospheric nitrogen and water steam.
Thus, through this chemical reaction which is produced after the burning into the exhaust system, the NOx emissions are reduced with up to 80% and in the same time the power of the engine increases.
How it works the SCR technlogy (part II)?
Due to the fact that the ammonia (NH3) is toxic in a free state, within the SCR system is used a solution that contains deionized water and urea (CO(NH2)2), the urea concentration being around 32,5%.
The automotive urea is obtained in special conditions, only at temperatures and high pressures( 150 °C, 50 bars) through an industrial process which mixes the ammonia (NH3) and the carbon dioxide (CO2).
The obtained urea is solid, with colorless crystals soluble into water.
The system is composed by the tank for urea, the control pc, the electrical pomp filling system, catalyst and injector.
What it is the International ISO 22241 standard?
From the desire to protect the environment and to preserve the air quality as pure as possible, the internationals regulations regarding the harmful emissions have been considerable improved lately.
When it comes to diesel engine vehicles, the nitrogen dioxides (NOx) and the diesel suspension particles are the first preoccupation and the efforts at international level have been focused on developing systems, technologies and procedures that can reduce them considerably.
Therefore, the SCR technology (Selective Catalityc Reduction) which use an urea solution ( technically nominated AUS32) or AdBlue as reduction agent, is considered to be the key technology to reduce the NOx emissions.
The quality of AdBlue used for this technology has to be standardized in order to ensure a good and stable functioning of SCR systems.
Thus, the ISO 22241 international standard establish the specifications for:
Quality requests – ISO22241-1
Testing methods – ISO22241-2
Packing, transport and storage- ISO22241-3
The filling interface – ISO22241- 4.
All the VDA Germany licensed producers ( The German Automotive Industry ) respects these internationals standards, the Association being extremely strict and it evaluates periodically through audits, in order to monitor the production, testing, packing, manipulation and storage standards.
News
___________
Articles
___________
Products
___________
Contact
___________
Program:
Monday - Friday
09.00 - 18.00
Saturday
09.00 - 14.00